What is the 550 Permanent Failure Error?
The 550 permanent failure error is an email error message that indicates your email was undelivered due to a permanent issue. In simpler terms, the recipient’s server slammed the door shut on your email and won’t let it in.
It differs from temporary bounce backs, which might happen due to a full mailbox or temporary server glitch. A 550 error suggests a more long-lasting problem that needs to be addressed.
What Causes a 550 Permanent Failure Error?
A 550 permanent failure error can be caused by issues on either the recipient’s side or your side (the sender).
On the Recipient’s End:
- Invalid Email Address: Maybe you mistyped the address, or it has become outdated.
- Full Mailbox: The recipient’s inbox has reached its storage limit and can’t accept more emails.
- Blocked Sender: The recipient or their email server has flagged your address or IP address as suspicious and is blocking your emails.
- Recipient Server Issues: If the recipient’s email server is facing downtime or having a technical problem that stops it from receiving emails.
On Your End (The Sender):
- Blacklisted Domain: If your email domain is flagged by anti-spam services as a source of spam, recipient servers might reject your emails automatically.
- SPF Issues: Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is a system that helps to identify the authorized senders for your domain. An incorrectly configured SPF record can make recipient servers suspicious of your emails.
These are some of the most common reasons for a 550 permanent failure error. The specific bounce back message you receive might contain additional details that can help to pinpoint the exact cause.
Read: What is a TLD (Top-Level Domain)? Explained
Ways to resolve a 550 permanent failure error?
A 550 permanent failure error can be frustrating, but there are steps you can take to resolve it depending on the cause. Check some approaches for both recipient-side and sender-side issues:
Recipient Issues:
- Verify Email Address: Double-check the recipient’s email address for typos or inaccuracies.
- Wait and Try Again: If the mailbox is full, try sending it again later when the recipient might have cleared some space.
- Contact Recipient: If you’re blocked or the recipient’s server has issues, try contacting them through another channel to explain the situation and see if they can unblock you or wait for the server problems to be resolved.
Sender Issues:
- Check Blacklist Status: Use online tools to see if your domain is blacklisted. If so, work with your email service provider to get delisted.
- Review SPF Record: Ensure your SPF record is configured correctly to avoid rejection, due to unauthorized sender issues. Your email service provider can assist you with this.
- Reduce Attachment Size: If your email contains large attachments, consider compressing them or using a file-sharing service instead.
- Review Email Content: Avoid excessive use of exclamation points, ALL CAPS, or spammy keywords that might trigger spam filters.
General Tips:
- Consult Bounce Back Message: The bounce back message might contain specific error codes or details that can help to identify the cause.
- Contact Email Service Provider: Your email service provider can offer more specific troubleshooting steps based on your email configuration and the bounce back message details.
By systematically checking these potential causes and applying the corresponding solutions, you can significantly improve your chances of successfully delivering your emails and avoiding 550 permanent failure errors.
Read: 6 Reasons to choose WordPress over Shopify for your online store
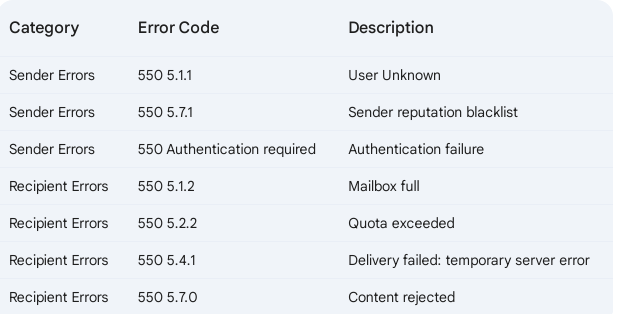
Common Types of 550 Errors: Explain
Here are some of the more common types of 550 errors categorized by whether they stem from sender or recipient server issues:
Closing Words
In conclusion, understanding the common causes of 550 Permanent Failure Errors is crucial for maintaining a robust email system. By implementing effective fixes such as updating DNS records, checking email content for compliance, and monitoring blacklists, organizations can mitigate these errors and ensure smooth communication.